
Contents
- 1 Rhythmic Patterns and Visual Cues in Leadership Coaching
- 1.1 Background Information
- 1.2 Rationale for the Study
- 1.3 Research Question
- 1.4 Research Aims/Objectives
- 1.5 Methods
- 1.6 Discussion
- 1.7 References
Rhythmic Patterns and Visual Cues in Leadership Coaching
Background Information
In recent times, there has been a notable increase in the number of techniques within the area of coaching, particularly in the realm of professional leadership. These methodologies have been developed with the intention of improving the effectiveness of the coaching process. These strategies frequently aim to cultivate a state of mind that is both balanced and concentrated. It is theorized that this state of mind might potentially decrease anxiety and improve attention, ultimately leading to more successful coaching results. The field of neuroscience has initiated investigations into the intricate mechanisms occurring within the brain that are influenced by diverse inputs, such as rhythmic patterns or visual signals.
Rationale for the Study
The current body of research work has initiated an examination of the advantages associated with a state of mind that is both balanced and focused within the context of coaching. However, there appears to be a lack of comprehensive understanding regarding the specific integration of rhythmic patterns or visual cues into coaching methodologies, and how such integration may contribute to their overall efficacy.
Research Question
Does the integration of rhythmic patterns or visual signals in coaching approaches have the potential to promote a state of mental equilibrium and attentiveness, leading to improved attention and less anxiety, thereby promoting more productive coaching results among professionals, particularly those in leadership positions?
Research Aims/Objectives
The objective of this study is to examine and evaluate established coaching protocols and procedures that have been recorded in academic literature. The focus will be on ways that try to cultivate a state of mind that is both balanced and focused, with specific emphasis on the setting of professional leadership.
- To explore neuroscientific data on rhythmic patterns, visuals, and coaching outcomes.
- To study the use in diverse cultures and reported adaptations.
Methods
1. Eligibility criteria – Exclusion and inclusion
The eligibility criteria for performing the systematic review will be based on the PICO framework which can assist in defining the intervention, comparison, and population of outcome characteristics by selecting a relevant set of secondary studies.
Application of the PICO Method
P as in population
Inclusion
- Professionals in leadership roles across different sectors which include educational, corporate, healthcare, and others.
- In order to perform a sub-group analysis, the professionals who take part in the leadership roles.
Exclusion
- The academic studies and evidence exclusively affect the non-professional populations (Kang, Zou&Weng, 2019).
As in Intervention
Inclusion
- Academic evidence utilizes techniques related to rhythmic breathing and visual stimuli having repeated patterns (Kang, Zou&Weng, 2019).
Exclusion
- Secondary sources incorporate visual and rhythmic breathing and visual stimuli with repeated patterns as a part of the coaching processes.
C as in Comparisons
Inclusion
- Studies compare the coaching methodologies by incorporating visual and rhythmic patterns.
Exclusion
- Studies that compares different coaching methodologies have visual patterns within including the traditional coaching group (Kang, Zou&Weng, 2019).
O as in Outcome
Inclusion
- Studies tracking results like increased concentration, less tension or anxiety, greater problem-solving skills, or enhanced decision-making
Exclusion
- Studies that don’t present pertinent outcome measures.
2. Search strategy
Data bases used
In order to provide a valid and accountable insight into the selected research topic, different databases have been used. In order to collect Grey data, Google Scholar has been taken into consideration, along with ProQuest. The Grey literature includes academic evidence such as; reports, thesis, conference process dings, and another form of non-traditional publications.
Keywords
The terms can be adopted to the specific databases and their syntax as required. Some of the example terms are addressed as below:
- Coaching
- Leadership
- Neurosciences
- Rhythmic Patterns
- Visual Cues
- Brain Function
- Anxiety
- Concentration
- Professional Development
- Cultural Context
- Grey Literature
MeSH Terms
Relevant MeSH terms for a systematic study on improving coaching results using rhythmic patterns or visual signals include “Coaching,” “Feedback, Sensory,” “Motor Skills,” “Learning,” “Visual Perception,” “Rhythm,” “Sensorimotor Integration,” “Training Outcome,” and “Sports.” By using rhythmic and visual interventions, these terms can be used to locate pertinent research and literature in the field of coaching and performance enhancement.
Study selections
Initial screening of the studies: All of the retrieved articles that are selected for this research will undergo an initial screening based on the title and abstracts.
Full-text review: The remaining papers will go through a full-text examination to determine their eligibility in accordance with the PICO standards.
Data extraction
The extraction of the data will be carried-out by using the standardized format. In this case the extracted data will include the following:
- Study specifics (title, authors, and year of publication)
- Methodology and study design
- Population characteristics (such as positions of authority and location)
- Information on the coaching technique, such as the type of rhythmic patterns and visual clues
- Information about the comparison group, if any
- outcome metrics and outcomes
- information on the cultural setting, if applicable
- Any other pertinent discoveries or observations
Data analysis (e.g. Narrative synthesis)
In this study, narrative synthesis entails methodically examining and summarising prior research on coaching effects using rhythmic patterns or visual clues. The data will be presented in a logical narrative, showing commonalities, trends, and linkages among the investigations. The goal of this synthesis method is to provide a thorough review of the field’s present state of knowledge
Results
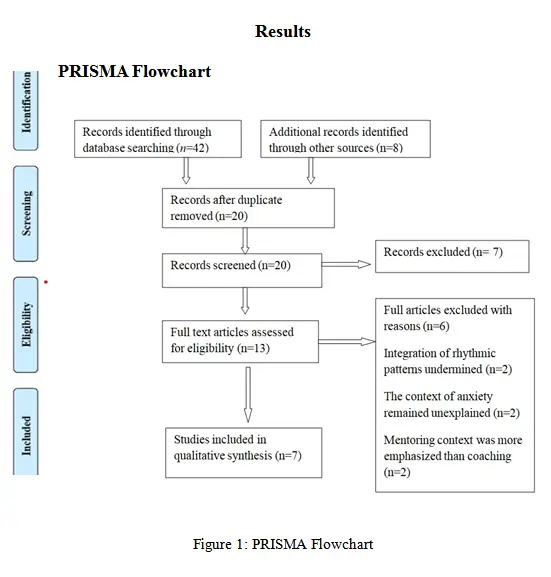
Figure 1: PRISMA Flowchart
Study selection and extraction outcomes
In terms of identifying the datasets and evidence, a total of 50 records have been initially identified through database searching and additional sources which inclines the grey literature. In this case, after removing the duplicates around 7 records are remained (Lai & McDowall, 2014). These records have been screened based on the titles and abstracts which have an accountable understanding.
Description of the included studies
The sources which are used in the research encompass a diverse range of studies across coaching psychology, coaching education, interventions, and sports coaching for assessing conditions like hypertension and dyslexia. The sources also contributes to the impact of rhythmic patterns and visual cues across different fields for providing a well-rounded foundation for the systematic review for enhancing different set of coaching outcomes.
Source 1: Systematic review of Coaching Psychology
In the selected research evidence from the qualitative studies has been given which specifically underscores the paramount necessity of trust in terms of coaching. They have found that mutual trust between the coaches and the coach plays a pivotal role in establishing efficient coaching support. Freedom and Perry’s case study have revealed that the coaches certainly feel unsupported until they perceive the coach as highly trustworthy and dependable at the same time (Lai & McDowall, 2014).
Source 2: Significant of coaching in medical education: A systematic literature review
Coaching can be found as an aspect that assists in gaining recognition of a certain number of valuable tools for medical education. Instead of the coaching process involving providing immediate and personalized feedback regarding the learner’s actions it aims for the maximization of the potential (Lovell, 2018). The following attached table from the selected journal evidence can provide a comprehensive understanding of inclusion and exclusionCriteria which need to be taken into consideration for performing the review of the coaching process.
Source3:Existing, informed and experienced realities of coaching processes by using transformation leadership
The leadership theory back in the 19th century laid a specific groundwork for the modern understanding of coaching and leadership specifically in terms of the TFL or the “Transformational leadership”. During the early times, some other leadership theories were available such as; Thomas Carlyle’s “Great Man theory” which suggests that great and efferent leaders are mostly born not made (Bruce-Martin, 2022).
It can be found that the importance of the shared values and effective collaboration taken place with the collaboration of TFL or transformational leadership theory includes some distinctive trades such as; confident, visionary, and uplifting the followers for achieving the ethical and moral goals in a specific manner.
Source4:Training and rehabilitation of students suffering from neurodevelopmental disorders
The selected source has highlighted that the BCI or the “Brain-Computer Interface” can be defined as a specific type of system that combines the usage of both hardware and software tools. It is designed to have a valuable extract of the information related to human signals (Papanastasiou et al. 2022). The BCI performs different functions including receiving, editing, utilizing, and sorting the brain wave signals. The brain signals have the ability to cover a wide range of frequencies such as; delta, Theta, Alpha, Beta, and Gamma. The BCI primarily pays attention to capturing oscillatory Electroencephalography Signals or the EEG which are produced by the extensive neural networks and relevant ERPs.
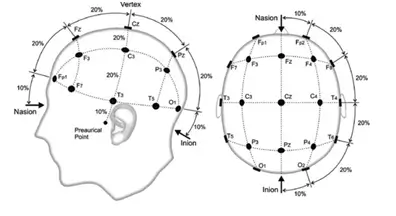
Figure: Different labels highlighting the regions of brain
Source: (Papanastasiou et al. 2020)
Source 5:Role of the auditory and visual components for reading based training
The selected research paper has addressed that Music has a significant potential to improve the reading skills of people who have developed dyslexia. Research has also indicated the fact that music-based interventions can deliver a positive impact on the phonological abilities of people and their auditory temporal processing for such individuals. It can be found that the connection in-between TS and “Temporal sampling theory”, has highlighted the necessity of a rhythmic sound processing system for phonological development (Cancer et al. 2022). The “Dyslexia” literature has also explored some other theories which include providing a “visuospatial attention deficits” and “magnocellular theory”.
Source 6:Interventions of interventions for the developmental dyslexia: Rhythmic reading training
Dyslexia is commonly associated with the difficulties found in phonological representation but the researchers explore different factors such as memory, attention, and perceptions. The growing consensus multiplies different types of causes and the factors that might contribute to reading disorders. This has led to some innovative treatments that indirectly enhance reading skills by targeting cognitive and perceptual abilities by making them linked to reading (Cancer et al. 2020). However, it can be found that the core challenge is to identify an effective intervention that not only improves reading but also ensures management of resources in an effective manner.
Source 7:Rhythmic speech in speech and language rehabilitation
The Rhythm plays a crucial role in terms of communication and taking part in social interactions. In terms of speech, the natural rhythm typically involves producing the 3 to 8 syllabi per second across different languages (Fujii et al. 2014). Primate studies have also shown that similar preferences for rhythmic patterns in terms of communicative gestures such as lip-smacking processes during face-to-face interactions are highly essential.
Report of the outcomes of data synthesis
The data synthesis which is performed by collecting evidence from different sources reveals valuable insights regarding the application of rhythmic patterns and the visual cues that are used for coaching across different contexts. These studies have collectively suggested that incorporating the elements can positively create a significant impact on the coaching outcomes.
Summary of findings table
| Sources | Link | Statistical data accessed |
| Source 1 | https://nrl.northumbria.ac.uk/id/eprint/50272/1/Bruce-Martin.Claire_phd%2804913189%29.pdf | The mean score for the DTLI subscale “contingent reward” (M=4.24, SD=0.76) was higher than the middle of the response scale. This pattern persisted across a number of groups, including athletes who were male (M=4.19, SD=0.77) and female (M=4.28, SD=0.75), coaches who were male or female (M=4.25, SD=0.76), and the environments in which players competed (participation/club M=4.23, SD=0.76; university M=4.31, SD=0.67; county/regional/national M=4.25, SD=0.75). |
| Source 2 | https://deptmedicine.utoronto.ca/sites/default/files/assets/files/coaching-review0.pdf | Reduced stress and a 41% decrease in doctors desiring to leave their profession were found in a 3-year quasi-experimental study. The study was given a middling quality rating. |
| Source 3 | https://nrl.northumbria.ac.uk/id/eprint/50272/1/Bruce-Martin.Claire_phd%2804913189%29.pdf | In quantitative research, adults (>18 years) made up 53.7% (n=22), teenagers (18 years) made up 24.4% (n=10), mixed age groups made up 14.6% (n=6), and non-labeled participants made up 7.3% (n=3). In qualitative investigations, 40% (n=2) didn’t specify the sample group, while 60% (n=3) involved adults. |
| Source 4 | https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S240584402031094X | According to Dennis and Hajcak (2009), there are no gender differences that are statistically significant; nevertheless, there is a significant interaction between Interpretation Type and Child Gender (F(1,16) = 5.32, p .05). Mu Power: F1,11 = 52.6, p .01; Theta and Beta: F1,11 = 57.4/38.3, p .01, according to Friedrich et al. (2015). Group X Time F(2, 27) = 3.313, p = 0.05 for practised performance; F(2, 27) = 6.224, p = 0.006 for creativity scale; F(2, 27) = 11.326 for communication subscale; and F(2, 26) = 20.36, p = 0.001 for reduction in commission mistakes. |
| Source 5 | https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpsyg.2020.01158/full | 24 Italian students with “developmental dyslexia” (8–14 years old; mean age 9.79) took part. An improvement in reading comprehension of roughly 1.2 z-scores was previously shown in studies. Power to identify such advances was 97%–98.5% with 12 participants. |
| Source 6 | https://www.mdpi.com/2076-3417/12/7/3360 | Reading speed did not increase in the No intervention control group (p = 0.57), but it did with Visual and Rhythm cues (p 0.001). There was a substantial Phase Condition interaction effect (F(2,110) = 83.4; p 0.001; 2 = 0.01). |
| Source 7 | https://www.proquest.com/docview/2292085296 | The left vPMC and nearby pIFG provide input to the bilateral vM1 in the DIVA model. These regions produce a “speech sound map” that translates spoken sounds into motor instructions. |
Table 1: Summary of the findings table
Source: As developed by the author
Discussion
Summary of the findings
Coaching, leadership theories, brain-computer interfaces (BCI), music-based therapies for dyslexia, and the function of rhythm in communication are just a few of the topics covered in the materials offered. The importance of trust in coaching relationships is emphasized, as is the “transformative ability” of coaching in medical education, the historical development of leadership theories, the capacity of BCI to extract information from human signals, and the potential advantages of music and “rhythmic interventions” in the treatment of dyslexia.
Critical analysis
It can be stated that the above findings offer a diverse range of insight regarding coaching, leadership, and the role of rhythmic communication and the learning process. While they have contributed towards some valuable data regarding their respective fields a critical analysis can reveal both the strengths and limitations of the sources as well.
The need for trust in coaching relationships is emphasized by Sources 1 and 2 in the context of coaching, as well as the transformative potential of coaching in medical education. These results support the notion that coaching is a potent tool for both professional and personal growth. Besides that other sources such as sources 3 and 4 have reflected some historical contexts by tracing the evolution of leadership theories. It sheds light on the importance of BCI in treating such problems by giving a brief review of its operations and the different kinds of brain signals it can record. Finally, Source 7 emphasizes the significance of rhythm in speech patterns and primate behaviour, providing insights into social interaction and communication. Although it adds important information, it doesn’t directly relate to coaching or leadership, thus its presence in this context seems a bit tangential.
Limitations and future consideration
Based on the above discussion it can be stated that limitations of the sources includes the need for having more depth of exploration of different topics. The source 1 lacks in giving specific details about the referenced studies, by making it challenging to evaluate the quality. Although Source 3 introduces transformational leadership, it might also investigate other leadership theories and their useful applications (Melo et al. 2020). Though they don’t go into detail, sources 5 and 6 offer encouraging insights into dyslexia therapies. Despite the fact that Source 7 emphasises the importance of rhythm in communication, it is still unclear how coaching and leadership relate to it specifically. Future studies should work to address these issues and provide a more thorough grasp of the subjects covered.
References
Bruce-Martin, C. (2022). Existing, Experienced and Informed Realities of Sport Coaching through Transformational Leadership. University of Northumbria at Newcastle (United Kingdom). From: https://nrl.northumbria.ac.uk/id/eprint/50272/1/Bruce-Martin.Claire_phd%2804913189%29.pdf
Cancer, A., Bonacina, S., Antonietti, A., Salandi, A., Molteni, M., &Lorusso, M. L. (2020). The effectiveness of interventions for developmental dyslexia: Rhythmic reading training compared with hemisphere-specific stimulation and action video games. Frontiers in Psychology, 11, 1158. From: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpsyg.2020.01158/full
Cancer, A., De Salvatore, M., Granocchio, E., Andreoli, L., Antonietti, A., &Sarti, D. (2022). The Role of Auditory and Visual Components in Reading Training: No Additional Effect of Synchronized Visual Cue in a Rhythm-Based Intervention for Dyslexia. Applied Sciences, 12(7), 3360. From: https://www.mdpi.com/2076-3417/12/7/3360
Fujii, Shinya; Wan and Catherine Y. (2014). The Role of Rhythm in Speech and Language Rehabilitation: The SEP Hypothesis. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience; Lausanne (Oct 13, 2014). DOI:10.3389/fnhum.2014.00777 From: https://www.proquest.com/docview/2292085296
Kang, T., Zou, S., &Weng, C. (2019). Pretraining to recognize PICO elements from randomized controlled trial literature. Studies in health technology and informatics, 264, 188. From: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6852618/
Lai, Y. L., & McDowall, A. (2014). A systematic review (SR) of coaching psychology: Focusing on the attributes of effective coaching psychologists. International Coaching Psychology Review, 9(2), 118-134. From: https://eprints.bbk.ac.uk/id/eprint/51154/1/51154.pdf
Lovell, B. (2018). What do we know about coaching in medical education? A literature review. Medical education, 52(4), 376-390. From: https://deptmedicine.utoronto.ca/sites/default/files/assets/files/coaching-review0.pdf
Melo, M., Gonçalves, G., Monteiro, P., Coelho, H., Vasconcelos-Raposo, J., &Bessa, M. (2020). Do multisensory stimuli benefit the virtual reality experience? A systematic review. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 28(2), 1428-1442. From: http://repositorio.inesctec.pt/bitstreams/4dfb6a10-4867-4321-acfe-237302efcf20/download
Papanastasiou, G., Drigas, A., Skianis, C., &Lytras, M. (2020). Brain computer interface based applications for training and rehabilitation of students with neurodevelopmental disorders. A literature review. Heliyon, 6(9), 13(8). From: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S240584402031094X
Researchgate (2023). Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International. From: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/PRISMA-flow-diagram-of-study-identification-and-selection-Correction-made-on-13-November_fig1_344376927
| This sample is written by Hannah Down, PhD in Nursing from University of Leeds, specialises in guiding students with nursing researches using scholarly journal articles. |
| This nursing sample is a model academic paper developed with the objective of supporting students with their study, research and for reference purposes only. The information included does not constitute any kind of medical advice or recommendation, and scenarios (if any) utilised are hypothetical and should be used for educational analysis in accordance with university academic integrity policy. |
Related samples
Self-Stigma & Help-Seeking in Depression | Rural Ireland Study
Family Presence in NICU: Benefits of Family-Centred Care
Communication in Health and Social Care
Professional Practice in Health and Social Care!!
Health Policy Response in The UK for Fighting Breast Cancer!!
Personalized Management of Multimorbidity: Addressing Hypertension and Complex Care in Aging Populations


